Global water bankruptcy begins: Is the world running out of water faster than we think?
The world has moved beyond a water crisis and into a state of global water bankruptcy, says a new flagship report released on Tuesday by UN researchers.
For decades, scientists, policymakers and the media warned of a “global water crisis,” implying temporary shock – followed by recovery.
What is now emerging in many regions, however, is a persistent shortage whereby water systems can no longer realistically return to their historical baselines.
“For much of the world, ‘normal’ is gone,” said Kaveh Madani, Director of the UN University Institute for Water, Environment and Health.
“This is not to kill hope but to encourage action and an honest admission of failure today to protect and enable tomorrow,” he told a press briefing in New York on Tuesday.
Unequal burdens
Mr. Madani emphasised that the findings do not suggest worldwide failure – but there are enough bankrupt or near-bankrupt systems, interconnected through trade, migration and geopolitical dependencies, that the global risk landscape has been fundamentally altered.
The burdens fall disproportionately on smallholder farmers, Indigenous Peoples, low-income urban residents and women and youth, while the benefits of overuse often accrued to more powerful actors.
From crisis to recovery?
The report introduces water bankruptcy as a condition defined by both insolvency and irreversibility.
Insolvency refers to withdrawing and polluting water beyond renewable inflows and safe depletion limits.
Irreversibility refers to the damage to key parts of water-related natural capital, such as wetlands and lakes, that makes restoration of the system to its initial conditions infeasible.
But all is not lost: comparing water action to finance, Madani said that bankruptcy is not the end of action.
“It is the start of a structured recovery plan: you stop the bleeding, protect essential services, restructure unsustainable claims, and invest in rebuilding,” he noted.
Costly tab
The world is rapidly depleting its natural “water savings accounts”, according to the study: more than half the world’s large lakes have declined since the early 1990’s, while around 35 per cent of natural wetlands have been lost since 1970, Madani said.
The human toll is already significant. Nearly three-quarters of the world’s population live in countries classified as water-insecure or critically water-insecure.
Around four billion people experience severe water scarcity for at least one month each year, while drought impacts cost an estimated $307 billion annually.
“If we continue to manage these failures as temporary ‘crises’ with short-term fixes, we will only deepen the ecological damage and fuel social conflict,” Madani warned.
Course corrections
The report calls for a transition from crisis response to bankruptcy management, grounded in honesty about the irreversibly of losses, protection of remaining water resources – and policies that match hydrological reality rather than past norms.
IBNS
Senior Staff Reporter at Northeast Herald, covering news from Tripura and Northeast India.
Related Articles
WHO prequalifies additional nOPV2 vaccine, strengthening global fight against polio
In a major boost for global public health, the World Health Organization (WHO) has prequalified an additional novel oral polio vaccine type 2 (nOPV2), a move that strengthens the international response to polio outbreaks, media reports said.
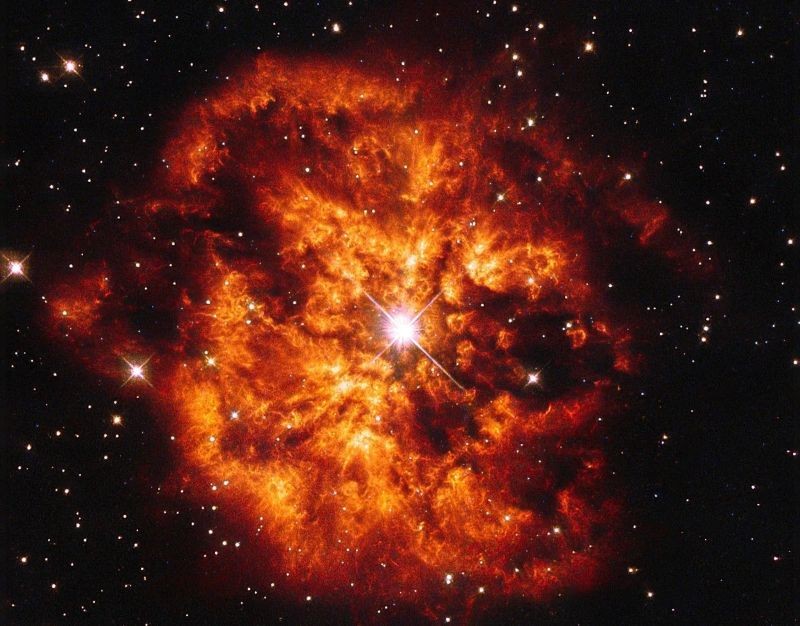

NASA Hubble captures stunning image of Wolf-Rayet Star Hen 2-427, surrounding nebula M1-67
A breathtaking new image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope reveals a rare cosmic pairing: the powerful star Hen 2-427, also known as WR 124, and the glowing nebula M1-67 that surrounds it.
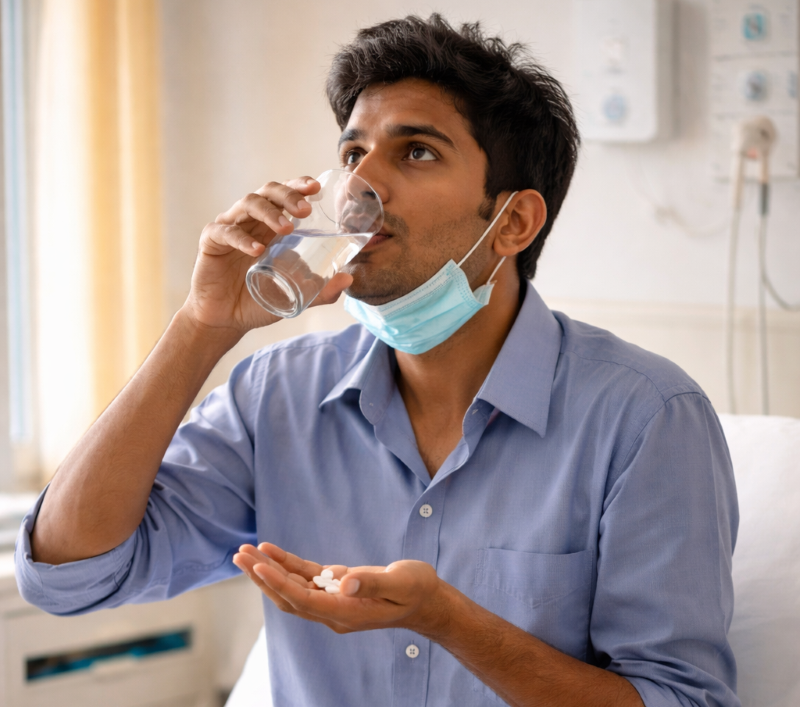

Game-changer for TB patients in India: Shorter oral regimens slash costs, ICMR finds
An economic evaluation published in the Indian Journal of Medical Research has demonstrated that shorter, six-month all-oral treatment regimens for multidrug-resistant and rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis (MDR/RR-TB) are cost-effective and offer improved health outcomes compared to the currently used longer regimens in India.
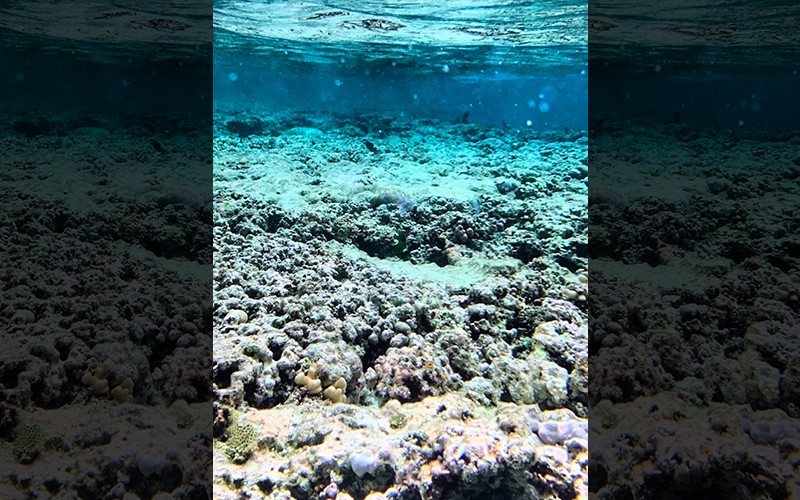

Underwater apocalypse: Half of all coral reefs severely bleached during 2014–2017 heatwave
Benefits to society from coral reefs, including fisheries, tourism, coastal protection, pharmaceutical discovery and more, are estimated at about $9.8 trillion per year.
Latest News

Indian student, missing for six days, found dead in California, consulate offers assistance to family

PM Modi invited to Dhaka as BNP’s Tarique Rahman set to take oath on Feb 17

Amid protests, Tripura CM favors Indian-origin script for Kokborok

Media is mirror of society must stay updated: CM

